Featured
How to Build a SaaS Sales Funnel
1. What is a Sales Funnel?
A sales funnel is a sequence of actions, events or stages that a user goes through before purchasing a product or service. Sales funnels are designed to allow marketers to track, record and optimise the sales process to improve results.
2. How to build a SaaS Sales Funnel
Your SaaS sales funnel is an essential part of your Apps success. If you’re offering SaaS apps then creating a repeatable, scalable and trackable sales funnel is one of the important steps that you need to take.
Sounds easy? Then think again. The sales funnel is where many start-ups transitioning into revenue generation struggle, and in many cases fail.
Before starting to build your funnel it’s worth first considering where you are in your app journey.
There’s a new way to deliver sales growth…
Don’t buy Sales Training until you’ve watched this video…
3. The three main stage of SaaS development
Unfortunately, in sales there is never a one size fits all solution, and the starting point for how to build a SaaS sales funnel is dependent on where you are, in the terms of the three main stages of a SaaS business?
Are you at:
Phase 1: the start of the journey whereby the Founder and primary team are still trying to establish product/market fit.
Phase 2: where the founder and primary team members have proven product/market fit and are proving they can implement systems and processes that others can use to sell.
Phase 3, the final hurdle where you have a proven product market fit, you’ve identified and proven the right systems and processes for scaling and you are now ready to scale your sales, focus on client acquisition and build up your MRR.
The strategies you use for building a SaaS sales funnel will vary depending on exactly what you learned in Step 1 above.
So for the purposes of this exercise, I will assume you are at Step 1. If you are still struggling to build a sales funnel at steps 2 and 3 then either you missed something at step 1, or something has changed that has made everything you learned at step 1 stop working.
4. Build a marketing funnel before your sales funnel
With any business it’s important that you provide the optimal conditions for your sales team to be successful. In the SaaS world it’s not enough to have a great website, you need a website that:
a) can be found by your products and services in the major search engines – Google, Bing, Yahoo & YouTube
b) can be found by the problems you solve in the major search engines – Google, Bing, Yahoo & YouTube
c) can convert web traffic to marketing qualified leads
Many companies ignore this and rush to build an outbound sales team. The fact is that every potential prospect that your outbound Team gets interested will then go to your website to do further research.
Unless the web experience is equal to or greater than the prospects experience with your outbound team they will immediately switch off.
To build a marketing funnel you must create “compelling user first content”. This is content that the user is actively searching for not the content that your sales and marketing team want to push.
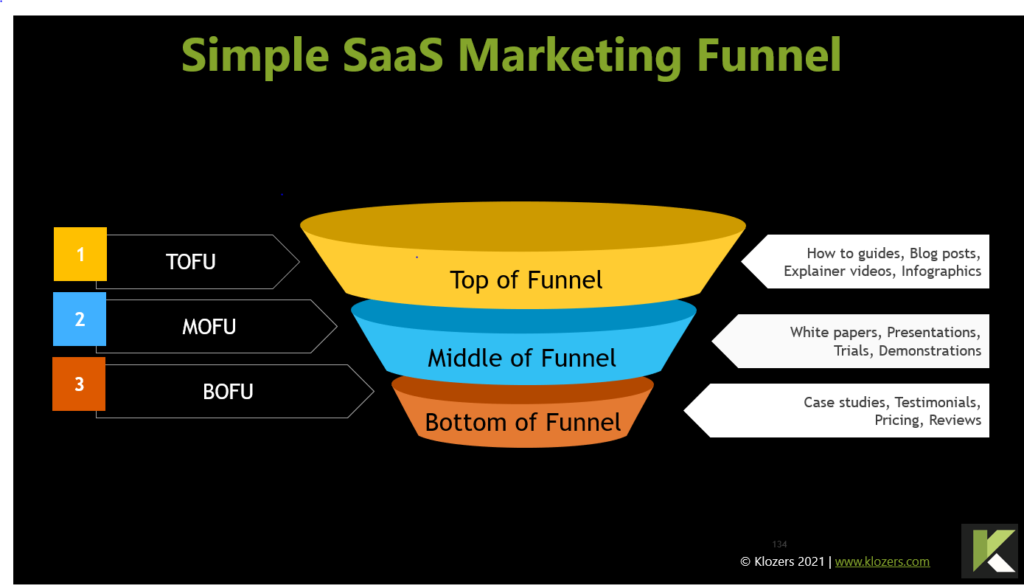
You SaaS marketing funnel is an essential part of your Inbound sales strategy. To do this successfully you will need to create high quality content at each stage of the buyer journey as shown below.
The content should subtly tell your brand story and the success you have brought to other users. Turn your early adopters into the Heroes not you.
TOFU – Top of funnel
The first part of your sales funnel otherwise known as TOFU is the awareness stage of the funnel. The prospect is aware of the problems they have and is investigating solutions.
Your website must have content that speaks to these problems and position your company as the Subject Matter Experts. The most popular content here would be:
How to guides
Explainer videos
Blog posts
Lead Magnets
At this stage, the prospect is in research mode, not buying mode and is simply gathering information.
Your prospect may not even be interested in solutions at this stage as they are still trying to accurately self-diagnose their own problems. It’s unlikely that your prospect will want to talk to sales at this stage.
We recommend you use marketing automation to track which articles/pages your prospects enter the site on as this is the problem that is top of mind for them. Knowing this can make it easier for sales to have a relevant conversation with them.
You may also have some success engaging the prospect with chatbots on your site, however many will want to remain anonymous at this stage.
Middle of Funnel
The middle of your sales funnel is when prospects start to evaluate specific solutions based on what they learned in stage 1. Middle of funnel content would include:
Presentations
Demonstrations
Case Studies
In practical terms they will have created some form of shortlist of potential suppliers, and they will then dig deeper into the details of each potential solution.
At this stage the prospect may still not engage with you as they are often simply researching on behalf of other people within their own organisation and their priority is still information gathering.
Bottom of Funnel
By the time your prospect has reached the bottom of your marketing funnel in many cases they have already “bought into” one particular supplier or solution.
They have made their decision largely on their web experience of the brand, your sales messaging and your ability to position yourself not only as a though leader but as a thought leader in that understands their problems.
Bottom of Funnel content would included things like:
Pricing
Comparison tables
Testimonials
Reviews
For simpler lower priced solutions you will find they are now ready to take a trial if you offer a strong Call to Action (CTA), whilst for the more expensive and complex solutions they will now engage with sales.
The image below shows where a simple marketing funnel transitions into a shopping cart and the more complex B2B sale transitions into a lead for sales.
Success lies not in choosing the right model, but building your own model based on data and trial and error.
Most marketing software now tracks user behaviour on your website and may use lead scoring to alert salespeople when the best time to pro-actively reach out to prospects.
From our own experience the timing is nearly always to early and a well-defined lead nurturing programme is equally effective.
In order to do this you should build into your marketing an at least three different lead magnets that will help you turn your web visitors into a subscriber so you can keep in touch.
5. Advertising to fill your Sales Funnel
Many companies successfully fill their sales funnel via advertising. Digital advertising has matured to a level that allows significant tracking and reporting allowing you to within a matter of weeks understand what your Conversion Ratio and CAC will be.
In the first instance we would advocate “Re-targeting Campaigns”. This is simply the process of placing adds in front of people who have already visited your website.
Studies show retargeting is seven times more effective than new campaigns which is why we advocate this as a starting point.
This strategy works extremely well with a strong content marketing campaign. The most popular add channel for B2B would be LinkedIn, however, many companies have also done well with Facebook and Instagram.
Needless to say this would be defined by your audience. Advertising can be used in simple funnels to drive sales and more complex ones to drive new enquiries for sales reps.
More complex sales may need a defined sequence whereby users click on and advert to receive a lead magnet with each lead costing $3.
If you subsequently manage to convert 5% of these new leads you can then attribute $60 per sale from advertising to your CAC.
You can build a trackable sequence or model from any activity not just advertising. For example, events, webinars and telesales allowing you to understand which activities are the most cost effective not only at filling your funnel, but actually converting into orders.
6. How to Build a SaaS Sales Funnel
Your sales funnel will vary depending on your sales strategy. Are you selling your App direct or are you selling through partners? Which channels have you decided to focus on initially?
1. Identify your Perfect Prospect Profile. This is the sales reps version of a marketing persona. It includes everything that a marketing persona would include, plus some additional information that helps sales understand and communicate at a deeper level with the prospect.
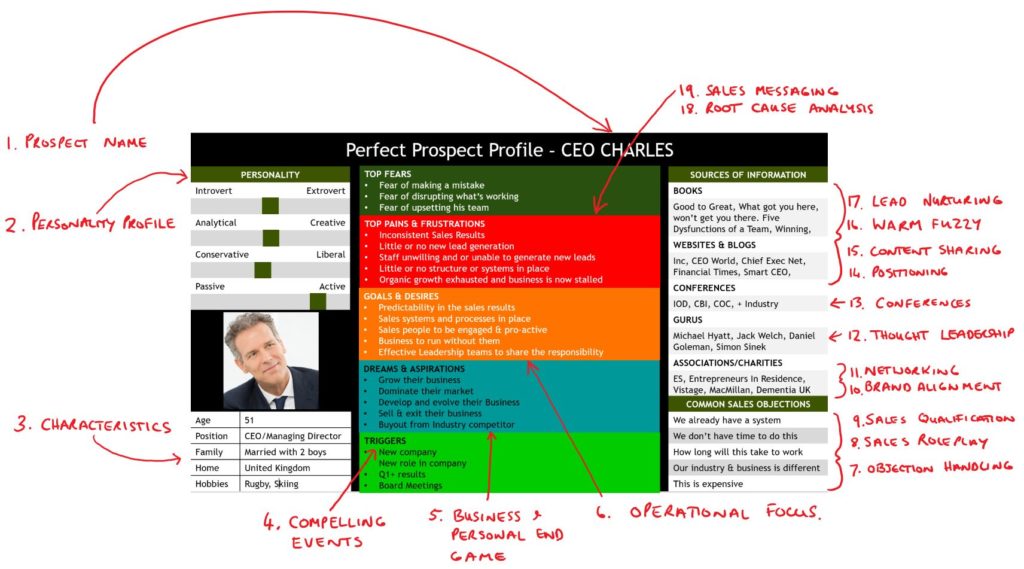
2. Build your sales messaging. Part of the product/market fit is understanding what business and or personal problem your product solves.
In our experience the most successful SaaS services are business solutions that solve business problems.
Once you understand how this relates to your own product/service at a deep level you can start to build your sales messaging.
This is the words and nuanced language you have proven that prospects connect with. It’s not enough to know about your own business and solutions, you should know about your customers.
You should know exactly how your solution helps your customer save money, make money and make their life easier.
3. Lead Generation Campaign.
Once you have identified your target prospects and built your sales messaging you will need to start work on a Lead Generation campaign.
There are two main approaches to Lead Generation as follows:
a) Inbound Lead Generation. Inbound lead generation campaigns are where the prospect contacts you first. The may fill out a form on your web page, telephone you or email you. In order to generate inbound sales leads you will need to do some form of content creation, ad campaigns, webinars, referral programmes or SEO.
b) Outbound lead generation. Outbound lead generation campaigns are where you reach out to prospects via telephone, email, direct mail, events or account based marketing. Outbound campaigns invariably means you will have to build an outbound says team which can be expensive.
The majority of SaaS companies use a combination of inbound and outbound, however, they nearly always have an emphasis on one more than the other.
As a very rough guide, SaaS services that are lower cost and targeting SMEs, are marketing led and have a predominantly Inbound focus.
SaaS services that are more expensing and targeting Mid-Market to Enterprise organisations will have a more sales led approach via Account Based Marketing.
7. What are the Stages of a SaaS Sales Funnel?

The stages of your sales funnel are simply a series of steps that your prospects move through to place an order.
These stages can vary greatly and there is no one funnel that you can apply to every app. Even if the stages are the same the method by which you move prospects through the funnel may vary.
Your sales funnel is a great place to start collecting data in order to measure performance and make improvements over time.
In general, prospects should move through the sales funnel as quickly as possible – this is called the sales cycle or pipe speed.
Measuring the speed that prospects move through the cycle allows you to identify blockages in your funnel and areas where prospects slow down.
These “sticking” points are where you should look to make improvements.
8. When do I demo my SaaS product to customers?
The timing of SaaS app demos within the sales process has been the subject of discussion for many companies.
The answer unfortunately to the question is “it depends”. Many companies successfully demo their app at the start of the sales process, however, there are equally many who demo at the start and then have their prospects disappear into the black hole of voice mail and unanswered emails.
In short the cheaper and simpler the solution, then the earlier in the process you can demo and the more expensive and complex the solution the demo should be pushed as far back in the selling process as possible.

The reality is that there is a tendency for Entrepreneurs and salespeople to rush to demo their app, hoping the demo will convince the prospect to sign up.
Even if the prospect is qualified and a good fit, a demo without any form of diagnosis of the prospects pain is in danger of losing the prospect.
Your prospect needs to know that you know and that you understand their world. This can only be achieved via intelligent and targeted questioning. If you want to speed the sale up, slow the sale down.
The demo is usually the salespersons greatest point of leverage and if you give it away to soon you will lose the leverage and in all likelihood the prospect.
As a general rule of thumb – push the app demo as far back in your sales process as possible.
Demos cost time and money especially for complex sales where more often than not a bespoke demo is required.
Any bespoke demo must only be delivered to the senior decision makers on the prospects buying team. If appropriate you can even have two demos within the sales process – there are no rules other than if it works do it.
Most sales reps make the mistake of using this part of the sales process to explain the benefits of the product in more detail.
When you’re telling you’re not selling. Use intelligent probing questions to get the prospect to tell you how the solution will solve their business pain.
You should avoid talking about features that you believe to be relevant to them. If you didn’t uncover this in the discovery stage of the sales process it’s inherently risky to introduce anything new further down the process.
For simpler lower priced solutions you will find they are now ready to take a trial, whilst for the more expensive and complex solutions they will now engage with a sales rep.
In order to demonstrate they have undertaken due diligence they will always speak to two or three potential suppliers.
This isn’t necessarily to beat a supplier down on price, but sometimes they need to validate to the wider purchasing group within their organisation why they have a preference.
App trials are also a good way to get users to sign up, however, the conversion ratio of trials to close is usually poor in most SaaS cases.
Depending on the pricing you could offer a managed trial, so they can evaluate your software while you manage them further down the sales process.
During a trial, the prospect can see how the product will work for them in practice. It’s important to time the trial wisely and ensure you have agreed in advance what happens if the trial is successful.
We’ve created the graphic above to try to explain visually how this might work for your organisation.
It’s worth noting in the example, the majority of your CAC will be marketing, whereas in the more complex funnel your costs will include marketing, sales + customer onboarding.
9. SaaS Sales Funnel examples
The sales funnels below are examples. You should NOT replicate these unless they fit with your sales process.
They are designed to be a starting point for those looking to develop a sales funnel.
As you can see from the graphic, there are many alternatives to the stages that go to make up your sales funnel depending on the type of funnel you are creating.
For purely digital funnels you could have:
Lead Magnet Landing page – where prospects arrive after clicking on your advert
Confirmation Page – confirming your free offer, trial or purchase
Upsell page – where prospects have an opportunity to add additional services or upgrade
Checkout page – where prospects pay for the service
Congrats or Thank You page – where you can sign post prospects with the appropriate next steps.

10. SaaS sales funnel metrics
When it comes to metrics we believe these are the common sales operations metrics and KPIs that most people are familiar with. Needless to say these metrics are important and you should be recording and reporting on them.
LTT – Lead to trial conversion
This is the number of leads who have converted to a trial.
DCR – Demo conversion ratio
The number of demos that successfully convert to the next stage in the sales process.
TTS – Trial to sale conversion
This is the number of prospects on the free trial who have converted to paying customers.
LTV – Lifetime Value of the customer
This is the average total value a customer will spend before leaving the service. Ironically this can be more difficult to measure the better your product is because, without customers leaving you will not know how long they stay and their total value to the business.
Churn – Number of customers leaving
Customers will leave and that’s not always a bad thing. If the customers who leave fit your ICP (Ideal Client Profile) then you have a problem. Customers who leave that don’t fit your ICP may be freeing up valuable resource that can be spent on your ICP.
MRR – Monthly recurring revenue
The monthly recurring revenue gives you an overview of your success, however, it’s only an overview and you need to look at the details within the data to gain a more accurate picture.
ARR – Annual recurring revenue
The annual recurring revenue gives a good overview of the business, but like the MRR you should study all the data to obtain a more accurate picture on the health of your venture.
Sales Cycle – The time from initial contact through to a closed order
This is typically short for lower value simpler solutions and longer for complex Enterprise sales. For example a sales to a Tier 1 bank may take 18 months from initial contact to close.
CAC – Customer Acquisition Cost
It’s important to understand how much it costs you to acquire a single customer. In an ideal world you would discover this in the initial phases of the business when you are proving the value proposition. Without this figure it’s impossible to put in the systems and processes to scale the business as you won’t know how much you can spend on the front end marketing and sales.
Negative Churn –
Negative churn is a powerful growth metric which indicates that the revenue from upselling and cross selling existing customers out strips the revenue lost when customers leave.
11. SaaS Proposal submissions
After the final demo, you should never offer to send a proposal.
Proposals cost time and money and if your prospect is interested they will ask you for a proposal.
If your prospect doesn’t ask you for a proposal then it tells you that they aren’t interested in working with you and you need to move back up the sales process to understand where you have gone wrong.
When the sales process stalls it’s rarely because of something you have done wrong at that moment – more often, it’s something you missed earlier on in the sales process.
Make sure you’re confident all the benefits of the software have been clearly explained to them and mapped out against their stated needs.
Where possible, always get your White Knight to help you co-create the proposal and sense check a draft version with them in advance of sending the official copy.
Before sending your proposal you must have a clear understanding of what the next steps are if you win or lose.
Without this you are most likely to spend the next three months chasing ghosts in voice mail.
12. Pricing your SaaS contracts
Many companies provide limited or no pricing at all on their website because they don’t want their competitors to see their pricing, or they think it will scare away potential customers.
You should be proud of your price and the value you bring. Let the competition undercut you and tie up all their resources on unprofitable deals.
People rarely buy the cheapest solution, so allow your prospects to undercut you.
If you’re still anxious about having your pricing on your website then think about how you feel when you are researching a solution you are interested in only to find the pricing page is littered with POA.
If you’re like most people you find this really annoying and quickly move on to the next potential supplier.
Lastly, another advantage of proudly displaying your pricing is that it qualifies out anyone who is not prepared to invest at that level.
This can save you lots of time and resources with prospects who simply have a different budget level.
There are numerous pricing strategies available to you, however, from our experience the only thing that is guaranteed, is that you will change your pricing.
As a basic rule of thumb if your prices are set too high for a short-term contract or paid trial, the prospect may fail to experience the full benefits of the software before the contract comes to an end, and they may decide not to renew.
Where possible you should reward prospects during the trial period for adding information and using the service.
For example, offer a shorter trial and incentivise users if they complete their profile/account set up.
Offer a further free period encourage them to use the product for example if they upload data into the system.
The idea is to “onboard” your new users step by step and make your product as sticky as possible.
If the prospect does want to go ahead you should use contracts with digital signature to speed up the sales process.
Never send contracts in emails or links to digital contracts as these can be easily ignored.
Arrange to get the prospect on the phone and talk through the contract with them. Once they have agreed to everything in the contract simply ask them to sign while you have them on the phone.
This way you retain control of the sales process.
13. Why the sales funnel is so important for SaaS providers
Many businesses have failed after struggling to implement a sales funnel. Marketing and selling SaaS products can be incredibly challenging, and chances are your target customers are already overwhelmed with offers from competing software vendors.
Think about which part of the buyers existing budget you are going to win revenue from. What direct or indirect competitors will you take budget away from?
You may be competing with some of the biggest and most powerful brands in the world that are providing generic solutions to the same problems you solve.
This means you need to offer something distinctive that your customers actually require.
A CB Insights study said 42% of SaaS start-ups fail because they’re offering products their target customers don’t need.
Convincing potential customers your software offers genuine value is essential.

14. Managing prospects expectations
Creating a sales funnel is all about building a journey all the way from web visitor, to subscriber and through demos and trails and ending with the contract being signed.
Your sales funnel should emphasise each of the key stages your prospects will travel through on their way to an agreement being made.
Be open, upfront and share the stages of the process in advance with your prospects.
You should pay close attention to any points of friction that might occur as your prospects travel through your sales pipeline.
This will give you the opportunity to make improvements to your funnel moving forward.
What’s most important is that you record all the data points in your sales funnel.
This will help you make decisions on facts rather than your gut feelings. It can take time for your sales funnel to become fully effective, and you may need to make several refinements before you have a truly optimised sales funnel.
Many customers don’t have a rich understanding of what they need when they first encounter you. Provide solutions not just products by helping prospects make the connection between the two.
What’s also true is users often buy what they want not what they need.
This is why it’s so important to ask targeted questions in order that you can accurately determine what their needs are so you can position your software in the most favourable way.
These questions will also tell you how near or far away they are to making a decision.
15. The Rise of SaaS solutions
It seems like everything in the world is now powered online by SaaS Applications. From Netflix and Amazon Prime to LinkedIn and Microsoft M365 we are now surrounded by SaaS solutions of one description or another.
Financially SaaS makes sense as it avoids heavy capital expenditure up front and de-risks the solution.
After all if it doesn’t work you are typically only ever locked in to a maximum of 12 months. Other advantages of SaaS include the way that it is normally quick to deploy and requires no maintenance on the part of the client.
Upgrades are normally delivered automatically, with clients generally being offered guaranteed levels of service.
Backups and data recovery are usually carried out on behalf of the client, so they can focus on what they do best, safe in the knowledge that everything’s being handled by the software developers themselves.
Lockdown has turbo charged SaaS
Remote working was on the rise even before the pandemic, so the fact that SaaS products allow individuals to work and collaborate from anywhere has only served to embed SaaS even deeper in our every day lives.
There are thousands of new products SaaS products being developed in every country around the world so competition is fierce, however, there is no apparent end to the appetite of consumers and business to SaaS solutions.
A coherent sales funnel could be the difference between your product being a viral success and being forced to return to the drawing board.
How to Write a Sales Plan in 8 Easy Steps (with FREE Template)
In this article we will cover...
1. How to write a Sales Plan
Few businesses manage to meet or exceed their sales goals without a sales plan, or should I say successfully create a Sales Plan and execute it.
Creating a sales plan helps you to establish your sales objectives, and outline the steps you will take to reach them.
A typical sales plan will include information on how the growth will be achieved (this is sometimes referred to as your sales strategies and tactics) and how sales will be measured.
Measuring the sales of your product or service may seem simple, but there are often important indicators and metrics other than revenue that can and should be used to measure the success of the execution of the sales plan.
Your plan may also feature details about target customers and their pain points, the sales process, roles and responsibilities, revenue targets, revenue goals, business goals and a sales and marketing strategy for your products and services.
Hopefully now you have a better understanding of the benefits of a sales plan you will take the next step and grab a free download our template in order that you can start creating a sales plan for your own business.
2. Different types of Sales Plans
Unfortunately, given all the differences between industries, companies and products there is no single plan that can be applied to every business. There are 3 main differences you should be aware of as follows:
1. Customer Base – are you selling to an established customer base where you need to manage existing accounts or are you selling to a greenfield territory where you need to focus on opening new accounts? In reality, it’s often a mixture of the two.
2. Market Movement – is the market stable enough to allow you to repeat what’s delivered your sales numbers in previous years or is the market changing and forcing you to change at the same time?
3. Business Strategy – the sales plan needs to meet or exceed the objectives of the business plan. The plan therefore needs to be aligned with the company mission and overall business strategy. If part of the business strategy is to divest risk from one income stream, the sales plan needs to reflect this.
Sales are the fuel that powers the ship, however it’s the business that decides where the ship is going.
3. Increasing Your Sales Revenues
At times sales can seem very complicated, however, it’s worth remembering there are only three ways to increase sales revenues as follows:
a) Increase sales by selling to accounts aligned with your ideal target customers
b) Increase sales by selling more to current customers
c) Raise your prices
The growth in your Sales plan must reflect at least one of the above, but preferably all three. You must also allow for “churn” as every business no matter how good they are will lose customers over time.
Even if you do nothing wrong customers will go bankrupt, they will be taken over, they will move away and you will lose business.
Reducing customer churn may well be part of your growth strategy. Anything you can do to increase your Customer Lifetime Value is always worthwhile and will stand you in good stead in the future.
4. Preparing for Success
Sales plans are primarily designed to help you achieve more sales. They should include information on what your current situation is, what you are aiming for and what you need to do to make your vision a reality.
Sales plans are like a roadmap your team can follow to achieve success. Without this roadmap they will take longer to achieve their targets as they move slower and possibly even in a different direction.
A more focused and driven team
A key benefit of every sales plan is that it can help make your team members more focused on achieving a specific goal, or series of goals.
Once a sales plan is in place, your team should have a firmer, more coherent idea of what your aims are. They should also have a more specific idea of what steps they personally need to take to achieve them.
Sales plans can also help you prevent a decline in sales over time by keeping your team focused and delivering a constant sense of purpose.
They can also help you make the most of your team’s specific capabilities and assign roles to the most suitable employees.
Creating confidence
Confidence is an important, yet often overlooked part of the sales success in any organisation.
A well written Sales Plan will give confidence and direction to the sales team and once you have a robust sales plan in place, you’re more likely to attract or keep investors and other stakeholders on-side.
The sales plan should also include information on the likely and possible challenges you envisage and how you plan to overcome them.
Clarity and coherence
Sales plans should be straightforward, so they can be easily understood by people outside the sales department.
There is no point filling your sales plan full of sales jargon which some team members may struggle to comprehend.
It’s essential that your sales plan firmly outlines your plans and goals for the period that it covers in an easy-to-read format.
If you would like help creating and implementing your sales plan we offer a full sales consultancy service and would love to talk to you about how we can work alongside your team to drive revenue growth.
5. Frameworks for a sales plan
We’ve put together a framework for your Sales Plan in Microsoft PowerPoint so it can double up as a presentation document. It includes easy to complete sections on:
1. Review – Learning what’s worked and what hasn’t from the previous year is an essential part of any sales plan. This way we can repeat or increase what’s been working and reduce, eliminate or adapt what didn’t work.
It’s also wise to look at your past data when setting targets. Do you have a good track record of hitting your targets? If you have failed to reach your aims in the past, do you know the reasons for this?
By closely assessing your past performance, you can optimise the chances of your latest campaign being a success and avoid setting unrealistic targets.
2. Sales Team – salespeople are a key part of the sales success in any organisation and should always be included in the plan.
In addition to showing past performance you should demonstrate how you plan to support them over the life of the plan by way of training and coaching.
Details of the training should be recorded in each employees PDP (Personal Development Plan) and Coaching should be recorded in individual coaching worksheets.
There may be times where every sales person has similar development needs but at as a minimum the coaching should always be bespoke.
3. Strategy – this is simply a high level statement on how you will approach selling to your market. The details such as goals, priorities and milestones of the strategy will be laid out in the Objectives section of the sales plan.
An example of a Strategy would be the Big Bets or Blockbuster strategy. Imagine if you were running a movie company and you were choosing what movies to invest $100,000,000 in over the next 12 months.
Would you take your $100,000,000 and invest £1 million dollars in 100 films or would you invest £10 million and try to create 10 blockbusters?
Perhaps your strategy is to move your customer base from Mid Market to Enterprise accounts. Your strategy might be to expand your portfolio to meet more of your customers needs and keep the competition out.
Your strategy may be the opposite and you might want to reduce and streamline your portfolio.
Removing choice allows you to focus sales and marketing resources and lower operating costs. We’re great fans of the Blockbuster strategy because we love the focus and simplicity it brings.
We accept there is an increased risk when you focus on fewer options, however, there should be some form of validation in your Blockbuster strategy. Will the next Bond movie be a hit? Well based on previous Bond movies yes.
So the majority (not all) Blockbusters should already be proven revenue streams that you are simply doubling down on.
4. SWOT analysis – thi is where you can document your Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats to help form and validate your sales strategy. Please remember the SWOT should only refer to your sales strategy.
The SWOT serves as proof that you and your team have undertaken some critical thinking around your sales strategy and have taken the time to think each aspect of the strategy through.
Once you have completed a SWOT analysis you can use the data to form a strategy that minimises the Weaknesses & Threats and maximises the strengths and opportunities.
5. Objectives – Your sales plan must be based around genuinely achievable targets. It will be much harder to get your team to embrace your sales plan if your aims are unrealistic or unreasonable.
It’s fine to be ambitious, but your goals still need to be realistic. Unrealistic or unachievable goals will only serve to demoralise the sales team and lead to them giving up.
Your aims and strategies need to be measurable so you can track the progress that you are making. You must include research that supports your aims, especially if your targets seem particularly ambitious.
Setting growth targets/objectives in the plan
Growth targets in a sales plan can vary wildly. Some sales plans are based on what the company wants to achieve over the next quarter, whilst others have longer-term 12 month goals.
It would be unusual to have a sales plan that was longer than 12 months as markets and customers can change so quickly.
Your sales plan needs to be agile enough to respond to these changes quickly. The best sales plans will feature detailed information on which activities need to take place and what kind of resources need to be used in order to generate success.
A simple method for sales forecasting would be to take the previous years monthly sales figures and then add 20% to each month. This provides a monthly sales target that accounts for any seasonal changes, and after 12 months will have delivered 20% annual growth.
It’s normally best practice to list separate sales objectives for:
product mix
new customers vs existing customers
sales by region
sales by vertical
individual sales reps
Whilst tracking each element may seem overkill, this allows you to quickly adapt your sales plan and implement contingency plans if required. For example, if one vertical is under-performing you may choose to divert resources into other verticals that are more active.

6. Sales Tactics and Techniques – after Strategy and planning comes the tactics. These are quite simply the approaches you will use to deliver the objectives of the sales plan.
Your sales tactics should call out the tasks and activities the sales team will be doing on a daily basis to implement the plan.
Tactics could be as simple as changing the sales messaging to match a new market or retraining customer service teams in up-selling existing accounts.
Perhaps you want your sales team to invest more time on Social media using tools like LinkedIn to identify new prospects or your interested in starting a cold email campaign.
7. Metrics – it’s important to agree on what success looks like how you will measure it before you start any project.
There are lots of great systems and tools available for this, however, you should make a list of tracking methods that you will be using for the duration of your plan.
These can include your selling strategies, techniques used for monitoring and performance metrics.
Where possible:
a) use existing systems and tools like CRMs that are already in place and being used, so you don’t get dragged into a software implementation project.
b) the recording of the measures should not create any additional workload for the salespeople as they are then less likely to complete them.
c) where possible use lead indicators and not lag indicators. Examples of a lead indicator could be the number of qualified new sales leads created and a lag indicator is the monthly revenue.
Whilst the revenue is important if we wait till the end of the month to get the revenue figures and we miss the target it’s too late.
Measuring the lead indicators allows us to take corrective action before the lag indicator is missed.
SaaS companies often track subscriptions to their app which is important but the lead indicator could be as simple as the number of visitors to the website.
You wil need to make a list of tracking methods that you will be using for the duration of your plan. These can include your selling strategies, techniques used for monitoring and performance metrics.
We use Sales Scorecards to record and track KPI’s, however, there are many different methods to track KPI’s from simple spreadsheets to online apps.
8. Budget – sales and selling costs money. Whether it’s a simple Linkedin Sales Navigator subscription or a 6 figure Expo in Las Vegas everything in sales costs money which needs to be budgeted for.
Budgets will vary greatly from one company to another, however you should always attempt to quantify the costs in advance.
Companies that do not have formalised budgets for Sales and work on an ad hoc basis are by nature lower down on the Sales Maturity model.
If you plan to spend a considerable figure during the period, you’ll need to justify this to your stakeholders. The plan should include detailed figures to illustrate where your budget will be going.
If you’re investing in new resources during the period, add an ROI analysis to your sales plan to help justify the investment.
You may also wish to budget for unforeseen costs such as recruitment, should a sales person leave unexpectedly you need to replace them.
If you’re not given the required budget, you may need to make changes to your sales plan, but you don’t necessarily need to scrap it completely.
6. Sales Plan Content
Your sales plan shouldn’t only consist of text. Wherever possible it’s worth have the document professional designed.
If you choose to use a template like ours you need to include your own branding as a minimum. It’s common for lists, tables, graphics, screenshots and charts to be used to convey key information about the company’s aims and the market you serve.
The sales plan should also feature research about what’s currently occurring in your industry This means it’s important to include statistics based on the latest research.
It’s also advisable to research your existing customers and targets market before you start creating your sales plan.
Depending on what sector you’re based in, there may be more demand from one market segment than there was in previous years.
Conversely, groups you were previously targeting may not be as interested in your products and services as they once were. Wherever possible do research so you can back up any positions you have taken.
Remember, your document doesn’t need to be incredibly formal, but it does need to be coherent and easy to comprehend.
7. Encouraging Buy In
Once you have completed your sales plan, you’ll need to present it not only to your team but your stakeholders and relevant managers too.
If you can’t get these on board, your plan is unlikely to be effective. The more convincing your sales plan is, the more enthusiasm you can generate.
The management is also more likely to release your budget if you can present an impressive well-thought-out sales plan.
With this in mind it’s always best to include other people in the creation of the Sales Plan. Getting buy-in from Sales people will be much easier if they helped create the document and senior management are much more likely to allocate budget if they have been included in the whole process.
With this in mind it’s worth asking your salespeople to create mini-plans and forecasts specific to their territory and then rolling these into the master plan.
This is a good way to develop ownership and responsibility within your sales team and provides a good reference point for future coaching.
A well-designed and executed sales plan can take your business to the next level. Just remember to keep it realistic and comprehensible so others ‘buy-in’ to it.
Whether you are a new business, a small business, a mid market or enterprise organisation the benefits of a well written sales plan are high. When done right your sales plan will position you for both short term and long term success.
Often an effective sales plan will play an important part with aligning the sales team’s activities and ensure everyone is working towards the same goals and moving forward.
Free Sales Plan Template
Download a free template so you can start enjoying the benefits of strategic and effective planning.
The free template is available for download as a Microsoft Word document to get you started.
This template is one of over 30 sales tools and templates available in our sales playbook.
Can we work with you?
Klozers provides B2B sales training and coaching throughout the world. Check out your nearest location or book a free consultation here.







