LinkedIn Workshops | Cracking the Code for Social Selling (en anglais)
Ateliers Linkedin - Question principale de Google
Qu'est-ce qu'un atelier LinkedIn ?
Un atelier LinkedIn est une session de formation qui se concentre sur l’apprentissage de l’utilisation efficace de LinkedIn. Il peut s’agir de sujets tels que la création d’un profil solide, la mise en réseau avec d’autres personnes et l’utilisation de LinkedIn pour trouver des opportunités d’emploi.
Un atelier LinkedIn peut être proposé par un organisme de formation professionnelle, un établissement d’enseignement supérieur ou une entreprise qui propose des formations sur les médias sociaux. Elle peut se dérouler en personne ou en ligne, en une seule session ou en une série de sessions. L’objectif d’un atelier LinkedIn est d’aider les participants à apprendre à utiliser LinkedIn à leur avantage dans leur vie professionnelle.
Dans cet article, nous allons couvrir...
Il existe une nouvelle façon d'augmenter les ventes...
N’achetez pas de formation à la vente avant d’avoir visionné cette vidéo…
1. Ateliers LinkedIn - Introduction
À l’ère du numérique, la vente sociale est plus pertinente que jamais. Il s’agit de se connecter et d’interagir avec les clients sur les réseaux de médias sociaux et LinkedIn est le père de tous ces réseaux. LinkedIn est une plateforme qui compte 720 millions de décideurs B2B et qui aide les entreprises à trouver et à créer des relations professionnelles.
Conçu à l’origine comme une plateforme de recherche d’emploi pour les recruteurs, LinkedIn est aujourd’hui le siège de la vente sociale et du développement commercial sur le web.
Grâce à nos ateliers de formation LinkedIn, vous apprendrez toutes les stratégies et tous les outils nécessaires pour attirer votre public cible. En outre, vous comprendrez les fonctionnalités spécifiques de LinkedIn pour développer des connexions professionnelles et renforcer votre présence personnelle et celle de votre entreprise sur la plateforme.
Dans ce billet, nous aborderons les principes de base de la vente sociale sur LinkedIn et la manière de bien s’y prendre.
Pour plus de détails sur les ateliers de formation LinkedIn et sur la manière de réserver un atelier, veuillez consulter la page Réserver un appel.
2. Créez un profil professionnel sur LinkedIn
Votre profil personnel LinkedIn est comme la page d’accueil d’un site web. Non seulement il met en valeur votre marque personnelle, mais il vous permet également de générer des prospects et de nouvelles affaires. Votre profil LinkedIn peut être trouvé par des relations existantes ainsi que par des clients potentiels, qui peuvent ainsi faire preuve de diligence avant de vous contacter.
LinkedIn propose un assistant pratique lors de l’inscription pour vous aider à compléter votre profil professionnel. Veillez à ne pas vous contenter d’ajouter votre expertise et à inclure des détails sur vos connaissances professionnelles et vos intérêts.
3. Construisez votre réseau professionnel
Sur LinkedIn, la plupart des gens se contentent de se connecter à de nouveaux clients potentiels et oublient de nouer des relations.
LinkedIn est une plateforme de mise en réseau d’entreprises. Une fois que vous êtes entré en contact avec des prospects, vous devez continuer à interagir avec eux (et non à leur vendre).
Comment procédez-vous ? Les principes de base sont simples : aimez, partagez et commentez leur contenu.
En réalité, plus vous essayez de vendre à quelqu’un, plus il vous résistera, surtout sur LinkedIn.
4. Interagir, interagir et encore interagir
La plupart des gens ne savent pas quelle est la meilleure façon de générer des prospects et de gagner de nouveaux contrats sur LinkedIn.
La façon la plus simple d’expliquer cela est de traiter LinkedIn comme un réseau traditionnel en personne – si vous ne le diriez pas ou ne le feriez pas en personne, alors ne le faites pas en ligne.
Ne pas interagir sur LinkedIn, c’est comme se rendre à un événement de réseautage traditionnel et rester dans le vestiaire tout l’après-midi.
Une fois que vous avez établi un lien entre votre profil de client idéal et votre public cible sur LinkedIn, vous devez interagir avec lui.
Entrez en contact avec d’autres professionnels du secteur et de nouveaux clients potentiels, et aimez, commentez et partagez leur contenu.
5. Mettez l'accent sur un contenu de qualité
Votre équipe marketing devrait déjà partager du contenu pertinent via votre page d’entreprise sur LinkedIn.
C’est pourquoi vous devriez réafficher ce document en y ajoutant vos propres idées et conseils.
Évitez de trop partager du contenu commercial sur vos produits et services, et concentrez-vous plutôt sur du contenu industriel qui est éducatif et qui aide à positionner votre entreprise en tant qu’expert en la matière.
Nous vous conseillons de ne pas dépasser un élément de contenu commercial tous les trois posts, et un minimum d’un élément de contenu commercial tous les cinq posts.
Si vous n’avez pas de contenu propre, vous pouvez en recueillir sur d’autres sites et partager le contenu de vos propres connexions.
6. Techniques de vente sociale - servir avant de vendre
Conformément à la loi de compensation d’Emersons sur LinkedIn, les personnes qui donnent gagnent.
Les clients potentiels n’achèteront pas chez vous tant qu’ils ne vous connaîtront pas, ne vous aimeront pas et ne vous feront pas confiance. Si vous voulez que les clients potentiels vous fassent confiance, vous devez d’abord leur apporter de la valeur. La plateforme LinkedIn est essentiellement une plateforme de marketing numérique qui vous permet d’entretenir des prospects et des clients potentiels.
Oui, vous pouvez acheter un outil d’automatisation LinkedIn et mener ce que nous appelons des campagnes de terre brûlée, mais ces outils nuisent à votre marque personnelle et à celle de votre entreprise, et font courir à votre compte le risque d’être fermé, car ils vont à l’encontre des règles de LinkedIn.
Vous devez également savoir que lorsque d’autres utilisateurs vous bloquent sur LinkedIn, vous êtes bloqué à vie, et pas seulement pendant la durée de votre emploi actuel. Cela rend la réussite dans les emplois futurs beaucoup plus difficile.
7. Créez un calendrier de contenu
Publier régulièrement du contenu est un excellent moyen de positionner votre entreprise sur LinkedIn et un calendrier de contenu est un élément important de votre planification.
D’après notre expérience, vous devriez publier au maximum un contenu par jour pour les marques nationales, et deux par jour pour les marques internationales, afin de tenir compte du décalage horaire.
Nous vous recommandons d’utiliser LinkedIn au minimum deux fois par semaine pour publier du contenu afin d’obtenir de bons résultats.
Selon une étude de Hubspot, les meilleurs moments pour publier votre contenu commercial et marketing sur LinkedIn sont les suivants :
De 12h à 15h, de 15h à 18h ou de 18h à 21h.
Mercredi, samedi et dimanche.
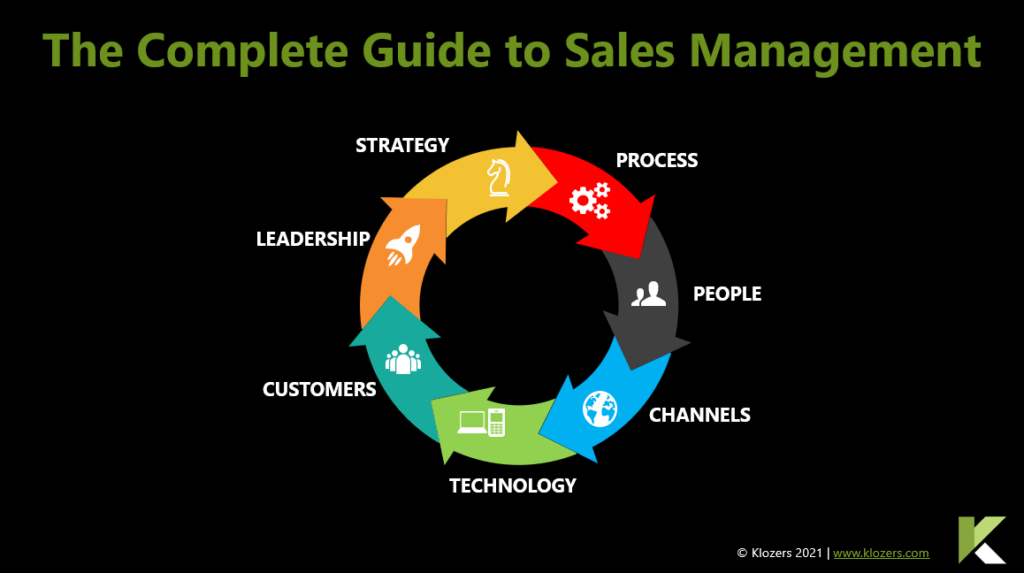
8. Construire une fondation
Du point de vue du développement commercial, si vous n’avez pas déjà une forte présence sur les médias sociaux, vos tactiques risquent de ne pas fonctionner à court terme.
Considérez LinkedIn comme un mini-site web où vous placez des informations pertinentes. Ces informations sont comme des graines, et pour en tirer profit, vous devez d’abord les nourrir et les entretenir régulièrement.
Ne semez pas les graines et n’arrivez pas le lendemain en espérant une récolte. Pourquoi les clients potentiels devraient-ils faire affaire avec vous dès le départ ? Partagez du contenu qui explique pourquoi.
9. Évaluer ce qui fonctionne
LinkedIn est un objectif en constante évolution et ce qui fonctionne peut changer. Outre le type de contenu marketing que vous publiez, évaluez le type de contenu. Formulaire court contre formulaire long, vidéo contre texte, carrousel contre PDF et sondages. Vous seriez surpris de constater à quel point les résultats peuvent être différents.
Comparaison des performances avec celles d’un message contenant une seule image et du texte :
Les posts de documents ont une portée de 2,2 à 3,4 fois supérieure.
Les sondages ont une portée 2,1 à 2,9 fois plus importante
Les posts du carrousel ont une portée de 1,8 à 2,3 fois supérieure.
Le texte et les images multiples (montage) ont une portée 1,2 à 1,6 fois supérieure.
10. Format de la formation
En tant qu’entreprise, nous croyons en l’apprentissage par le travail. Ce style d’enseignement vise à faire sortir les apprenants de la salle de classe et à leur permettre d’apprendre par la pratique.
Nos formations LinkedIn sont conçues en fonction de vos priorités d’apprentissage et, dans la mesure du possible, nous adaptons le contenu de la formation à vos besoins. Plutôt que de se baser sur la théorie, chaque atelier propose une approche pratique de l’utilisation de LinkedIn.
Chaque cours de formation est dispensé soit en personne, soit à distance en ligne par le biais d’un atelier d’une journée ou d’une demi-journée.
11. Ateliers LinkedIn
Klozers propose des ateliers de formation LinkedIn en personne et à distance en ligne. Notre formation LinkedIn donnera à votre équipe la formation complète dont elle a besoin pour identifier les clients potentiels et entrer en contact avec eux. et vendez-leur de la manière la plus efficace et la moins polluante possible.
Nos formateurs en vente vous aideront à concevoir et à organiser des ateliers de formation adaptés à votre entreprise.
Chaque session s’appuiera sur les connaissances existantes de votre équipe de développement commercial et sur la manière dont elle utilise LinkedIn. Nous apportons un soutien continu à votre personnel et à votre équipe dirigeante afin de vous permettre d’entrer en contact avec davantage de nouveaux clients potentiels et de générer des ventes et des revenus réels.
Si vous êtes intéressé et souhaitez en savoir plus sur notre formation LinkedIn, vous pouvez prendre rendez-vous avec l’un de nos spécialistes de la formation LinkedIn ici.
“Une expérience d’apprentissage fantastique”
Amanda – Responsable de compte