Why Non “Salesy” Sales Training for Consultants Works
In this article we will cover...
There’s a new way to deliver sales growth…
Don’t buy Sales Training until you’ve watched this video…
1. Why Being Salesy Doesn’t Work for Consultants
Being Salesy is forcing your beliefs and opinions on why someone should buy a product or service from you. This rarely works because the approach is very off-putting for the person receiving on the receiving end and in most cases damages the Consultants personal brand in addition to the brand of the business.
Being Salesy clashes with our personal values which are the unwritten rules that guide the way we live and behave. When we are living and acting in congruence with our personal values people are the most productive and the most successful which is why being “salesy” doesn’t work for consultants or anyone else for that matter.
Consultants are not Sales People, they are experts in their chosen field and any sales training should be bespoke and reflect and leverage that expertise.
2. Selling Tips for Consultants Who are Introverts
Roughly one third of the population are introverts which means they are more likely to be uncomfortable around other people whether they are selling or not.
Introverts can make great salespeople as they are usually good listeners, good at building relationships and have high level of self awareness.
There are some practical steps that Consultants who believe themselves to be introverts can take to to help themselves enjoy the experience of selling more.

People who are introverts have a “self-as-story”. This self story reinforces negative beliefs such as they are introverted, not good with people and cannot sell.
It’s important to develop a new and believable “self-as-story” with more positive beliefs such as “I am not an introvert I am an Ambivert”.
Ambiverts are the third of the population who sit in the middle between introverts and extroverts. “I am good with people and I enjoying spending time helping others.”
Most human beings are by nature kind and well-meaning so this is again a believable statement.
“My job is not to sell but instead to be of service, help people and create the right conditions for someone to buy; if they want to.”
3. Sales Training for Consultants
We often are asked to train what we call Non-Selling Professionals in new selling techniques and these are people in a business where the sales function is not their primary role, they could be Consultants, but equally, they could be Lawyers, Engineers, Analysts, Accountants, Developers & Architects etc.
In most cases when we first meet them they proclaim that they could never be a salesperson – the reality is that humility is one of the traits that means that they absolutely could be a great salesperson.
Unfortunately, what’s holding these people back is that the publics’ perception of a salesperson is largely negative and the type of adjectives the public use, when asked to describe a salesperson, are words like “liar”, “selfish”, “talks too much”, “money-grabber” and “annoying”.
The reality is that most salespeople are nothing like this, however, sometimes we pay the price for those that go before us and unfortunately there are, albeit a small number of salespeople, who are like that. If you think about it though, those traits are hardly a recipe for success.
4. How to get sales leads without picking up the phone
After spending years trying to train and coach consultants, engineers and technical people from every different industry, we came to the realisation that nothing we could ever do would motivate them to pick up the phone and make a cold call consistently.
If we showed them how to make a cold call that won them a $1 million dollar order they would still prefer to come in the next day and work at their desktops. These same people, however, would be more than happy to take inbound calls and talk to strangers who had called them.
The answer to the challenge was easy then – get their phones to ring and get their email to ping. If you talk to anyone in B2B marketing they will probably say quite rightly that generating a consistent flow of inbound leads is not easy.
We worked with our own team to develop a new strategy around this and worked to implement this strategy into our own business to prove it works and to gather some good data.
What is this strategy and can it work for me? In simple terms the strategy involves leveraging the knowledge and expertise of the consultants, and position them and their company as SME’ s (Subject Matter Experts). We then help them develop thought leadership content that buyers were interested in.
We then help them take that knowledge and place it on their website in a way that can be easily found and ranked on Page 1 of Google – just the same way you found this article. This then creates a steady stream of self qualified sales leads who have already bought into the expertise of your consultants and keen to engage further.
What’s more unlike pay per click ads these articles create a steady flow of new leads that fuel future growth at no cost. Once the content is published that’s it.
No cold calls, no outbound phone calls of any sort. In fact, in some cases our clients are now closing deals via email.
If this approach interests you and you would like to learn more please contact us for further details.
5. Training Sessions for Sales Consultants
In most cases sales training for Consultants is delivered over 1 & 2-day courses. This can work however in our experience, Consultants can immediately feel defensive if they are told they need training as they are nearly always mature adults and often have had a negative experience from previous Sales Training programmes they have attended.
The best way around this is to choose sales training for Consultants that is specifically designed for Consultants and content that highlights the skills and experience of the Consultants. The trainer should have experience of training a wide variety of non-selling professionals and be able to address the specific learning styles and needs of this type of audience.
What can be equally productive is running workshops where the Consultants get to choose what they feel would benefit them most. This way they feel more empowered as they have chosen the content and by definition, the content should be more targeted and relevant.
The only drawback to this is that this requires an experienced facilitator/trainer who knows the answers to the Consultants Sales Challenges from memory and can articulate them without a PowerPoint. If the trainer has to stop the session to look up the answers in a textbook or slide deck they will lose all credibility.
These workshops should have defined outcomes with action plans to make sure they are more than just a talking shop and deliver real impact for the Consultants and the company.

6. Sales Training Tips for Sales Consultants
Most people have a common misconception that selling is all about closing and forcing people to make decisions that they might not want to make. In reality, this couldn’t be further from the truth as the most successful salespeople simply don’t do this because they know it doesn’t work and in many cases destroys any trust or relationship that they have with the prospect.
In most cases, traditional Sales Training for Consultants won’t work because the techniques they use go against the Values & Beliefs of the Consultants. No matter how good the trainer is unless the content is based on actions that are congruent with the beliefs and values of the Consultant it will simply be a waste of everyone’s time and money.
What will work however is if the training is designed to position the Consultants as Trusted Advisors to their prospects and the sales activities are aligned with positioning them as Thought Leaders in their Industry.
The following sales tips help Consultants & Non-Selling Professionals understand that Professional Selling is more about building trust and relationships than it is about “Closing” prospects.
To sell more consultants should focus on building TRUST
T = Time
R = Reliability
U = Unselfishness
S = Soundness
T = Truthfulness
Time
Set Goals and manage your own time – be effective, not busy. Be respectful of your clients’ time, turn up on time to meetings, prepare before meetings to get the most from them. Spend time with clients to help them. Focus your time on your best prospects.
Reliability
Get a plan and stick to it, sales plans, communications plans and account plans. Many sales are lost when you are back in your own office. Respond to every email within 24 hours, manage expectations and take ownership of problems and follow up.
Unselfishness
Listen, empathise and give, yes give, as in Emersons Law of Compensation. Stop trying to sell and start trying to help, have conversations, not sales pitches. Recognise when there is no fit and walk away – never force the sale. Pass on referrals and give recommendations.
Soundness
Become an expert in your field. Be the “go-to” person in your industry that people refer others to. Create your own personal development plan and learn as much as you can about yourself, your customers and your customers’ customers. Mentor, coach and help others.
Truthfulness
Be true to yourself. Have those difficult conversations with family, friends, colleagues and customers. Losing some sales, losing some battles will help you win the war. Nurture and grow your integrity, self-respect and self-belief. Be authentic and true to yourself.
These Sales Techniques are not glamorous, and they might not produce an overnight transformation however they do work. Together you will see these five areas form the basis of TRUST. Selling without trust may be possible, but it is extremely hard work and will, without doubt, limit your success. In business, the antithesis of trust is a risk, and every Buyer, every CEO, every organisation will pay more for a solution that is perceived to mitigate risk. Building and sustaining TRUST is the foundation of Mastery in sales, although many of our clients have asked us to help embed these “selling techniques” throughout their organisation, not just sales.
7. Sales Training for Professional Services
Selling Professional Services can be very different from selling as a Consultant because in many cases when you are selling Professional Services the salesperson is the product.
In B2B more so than B2C, buyers rarely purchase anything from a salesperson they don’t like or trust. There are exceptions to this when the Brand Power of the product or service is very strong, for example it doesn’t take the salesperson of the year to sell Microsoft Technical Services because the power of the Microsoft brand has pre-sold most people before they go into the sales meeting and the product is Microsoft, not the Consultant.
For Consultants who do not represent a big brand like Microsoft, Deloitte, or Bain & Co, in most cases they are the brand, they are the product, and they have to work even harder to win the sale.
In many cases what is more productive for Consultants is to stop trying to sell and focus all their energies on trying to help the prospect.
We recommend a Consultative Sales Approach which focuses the sales conversation around 5 critical questions.
- What are the symptoms of the business problem?
Prospects find it easier to identify symptoms however it’s the role of the expert to ask questions and dig deeper.
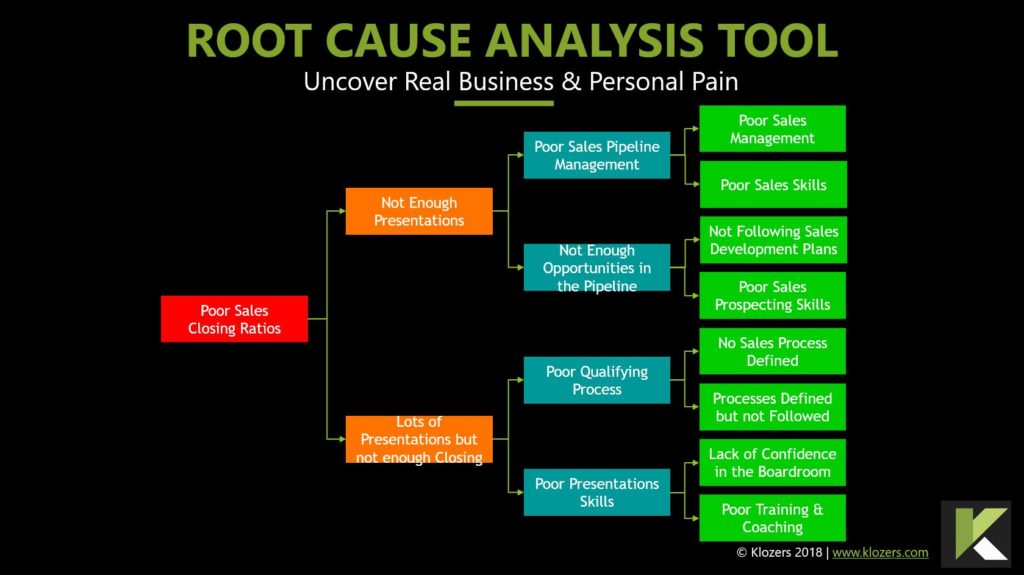
- What is the Root Cause of the Problem?
The Consultant should use Root Cause Analysis techniques to identify the underlying causes of the problems.
- How is this problem impacting the business?
These questions should focus on what way the problem limits growth, profits or damage the brand in any way.
- Financial Impact
The consultant and the prospect need to do a basic cost-benefit analysis to ensure the client will see a return on any investment they make.
- Personal Impact
Lastly, the Consultant needs to uncover any personal motives or drivers that are important to the client.
Often by simply asking these questions, the Consultant will get the opportunity to position themselves as the expert at the same time building rapport and trust with the prospect.

8. Sales Training Courses for Consultants
We have training and coaching courses available to help your consultants overcome their sales challenges.
We deliver our sales training and coaching via our Online Sales gym so we can provide support throughout and after the training period.
This helps you embed the new skills and sales behaviours in your organisation to maximise the impact of our training.
You can learn more about our Sales Training for Consultants via the following articles:
Consultative Sales process here